Does Tobacco Cause Cancer? It does something more than that.
As we dwell more and more into does tobacco cause cancer, we would only find out numerous studies that support the fact that it does. It also increased the risk of getting cancer at the same time.
31 May is marked as the WORLD NO TOBACCO DAY every year. This relies on the fact that the major population of the country is tobacco users – with or without being aware of its consequences. The tobacco industry is said to have the highest growth rate ranked seventh among the 23 industries tracked by the Central Statistics Office’s Index of Industrial Production. The tobacco industry had expanded 5.5% in February 2020 in terms of output as compared to last year. It had expanded at 22.7% in January 2020.
According to the World Health Organization, tobacco kills more than 7 million people annually. Over 6 million deaths are because of direct consumption, whereas 890,000 are because of passive smoking. Nearly 100 million premature deaths have been logged in the 20th century and are set to rise to 1 billion by the 21st century. Smoking kills around one million people in India annually and is the fourth prominent cause of non-communicable diseases such as cancer and heart disorders, which is responsible for 53% of deaths in India.
Why does tobacco cause so many deaths? What changes occur in the body when exposed to tobacco? Does it lead to cancer?
It is a known fact that smoking leads to lung cancer. Almost 9 out of 10 cases of lung cancer have been caused due to smoking. There are two types of tobacco use:
- Smoking tobacco: Tobacco smoke contains chemicals like formaldehyde, hydrogen cyanide, arsenic, lead, benzene, ammonia, and radioactive elements, etc. which are known to cause cancer. These cancer-causing chemicals are referred to as carcinogens. Nicotine, the addictive drug (key stimulant) is one of the harshest chemicals in tobacco smoke.
- Smokeless tobacco: Snuff and chewing tobacco are placed in the mouth/nose. Products contain a variety of potentially harmful chemicals, including high levels of TSNAs (Tobacco-specific nitrosamines), radioactive substances, benzo [a]pyrene, and other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Carcinogens absorbed through the mouth are linked to oral cancers.
To counter these deleterious effects of tobacco use, e-cigarettes and other electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) are used as substitutes for cigarettes or other tobacco products. Marketers of e-cigarettes and other ENDS often claim the ingredients are safe, but the aerosols contain addictive nicotine, flavorings, and a variety of other chemicals, some known to be toxic or to cause cancer.
 Tobacco and cancer. (2020, July 10). Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.
Tobacco and cancer. (2020, July 10). Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.
A normal lung contains immune cells called alveolar macrophages which help in eliminating foreign bodies or toxic substances which have escaped the body’s defence systems and entered the lungs. When a person smokes and the smoke enters the lungs, it triggers a higher inflow of macrophages (detect microbes) and neutrophils (WBC – deals with infection). Smoking directly exposes the epithelial tissue to at least 60 potent chemical carcinogens with the ability to cause DNA damage to the larynx, bronchi, and lung epithelial cells.
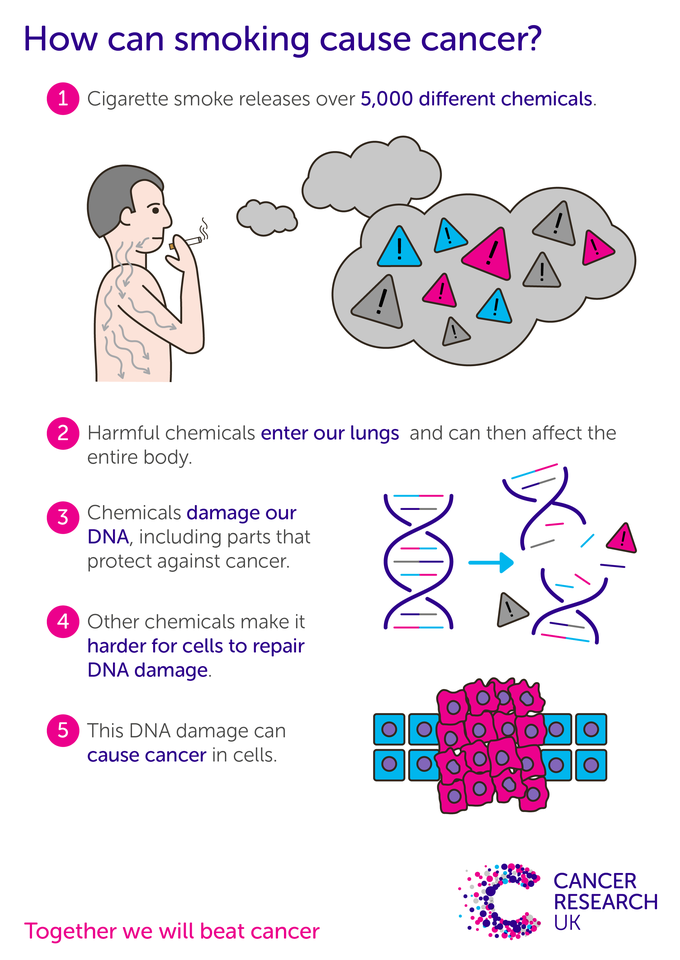 How does smoking cause cancer? (2020, August 24). Cancer Research UK.
How does smoking cause cancer? (2020, August 24). Cancer Research UK.
Tar and nicotine present in tobacco products have immunosuppressive effects on the innate immune response. It hinders the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus compromising pathogen elimination by neutrophils and other cells of the innate immunity.
The epithelial cell damage and the suppressive role of nicotine on the apoptosis of the cell (programmed cell death) is an important factor for the survival of malignant cells and the formation of numerous epithelial lesions known as field mutations. Apoptosis is the main protective cellular mechanism against cell proliferation showing irreversible DNA damage. Numerous field mutations are found across each cell surrounded by an inflammatory response.
Chronic inflammation is a major consequence of smoking that also leads to increased cell proliferation which finally results in cancer cells. Eventually, one of those field mutations escapes and starts promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels which nurture the cancer cells) and rapid cell proliferation, resulting in an epithelial tumor.
Carcinogens present in tobacco products have an influential role in altering the genome of immune cells, whether by implanting chemical adducts in the cellular DNA or by inducing irreversible genetic damage. Tobacco smoking or consumption continues to be a huge public health challenge and a social and economic burden to nations, families, and individuals who lose their health, productivity, and their lives under nicotine addiction.
Prevention is always said to be better than cure. You should get yourself tested to protect yourself against any form of cancer.
REFERENCES:
- Tobacco output expanded by 5.5% in Feb 2020. (2020, April 9). The Mint.
- World no tobacco day: 34.6 percent of adults in India are smokers. (2019, September 17). India Today.
- Nise H. Yamaguchi. (2019, May). Smoking, immunity, and DNA damage. PubMed Central (PMC)

 Kindly fill the form below to download our Liquid Biopsy Portfolio brochure :
Kindly fill the form below to download our Liquid Biopsy Portfolio brochure :